聊聊動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源
前言
咱們星球中的商城系統(tǒng)中使用了動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的功能,實(shí)現(xiàn)了分庫分表的訂單庫的讀庫和寫庫的自動切換。
有球友反饋說,對動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源不太熟悉。
今天這篇文章就專門跟大家一起聊聊動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源,希望對你會有所幫助。
一、為什么需要動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源?
有些小伙伴在開發(fā)中可能會遇到這樣的場景:一個系統(tǒng)需要同時訪問多個數(shù)據(jù)庫,或者需要根據(jù)業(yè)務(wù)參數(shù)動態(tài)選擇數(shù)據(jù)源。這
時候,傳統(tǒng)的單數(shù)據(jù)源配置就顯得力不從心了。
1.1 傳統(tǒng)多數(shù)據(jù)源的問題
傳統(tǒng)方式的多個數(shù)據(jù)源配置,硬編碼,不靈活。
例如下面這樣:
@Configuration
public class TraditionalDataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSource primaryDataSource() {
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1");
dataSource.setUsername("user1");
dataSource.setPassword("pass1");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public DataSource secondaryDataSource() {
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2");
dataSource.setUsername("user2");
dataSource.setPassword("pass2");
return dataSource;
}
}使用時需要手動管理數(shù)據(jù)源。
@Repository
public class TraditionalUserDao {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("primaryDataSource")
private DataSource primaryDataSource;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("secondaryDataSource")
private DataSource secondaryDataSource;
public User findUserFromPrimary(Long id) {
// 需要手動獲取連接、處理異常、關(guān)閉連接
try (Connection conn = primaryDataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?")) {
stmt.setLong(1, id);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery();
// 處理結(jié)果集...
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("查詢失敗", e);
}
}
}每個方法都要重復(fù)這樣的模板代碼,需要手動指定數(shù)據(jù)源,很麻煩。
那么,如何做優(yōu)化呢?
1.2 動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的優(yōu)勢
接下來,我們一起看看使用動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源后的優(yōu)雅代碼。
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
// 根據(jù)租戶ID自動選擇數(shù)據(jù)源
public User findUserByTenant(Long userId, String tenantId) {
// 設(shè)置數(shù)據(jù)源上下文
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(tenantId);
try {
return userMapper.selectById(userId);
} finally {
// 清理上下文
DataSourceContextHolder.clear();
}
}
// 多租戶數(shù)據(jù)聚合查詢
public UserAggregateInfo getUserAggregateInfo(Long userId) {
UserAggregateInfo result = new UserAggregateInfo();
// 查詢主庫
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource("master");
result.setBaseInfo(userMapper.selectById(userId));
// 查詢歸檔庫
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource("archive");
result.setHistory(userMapper.selectHistory(userId));
// 查詢統(tǒng)計(jì)庫
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource("stats");
result.setStatistics(userMapper.selectStats(userId));
return result;
}
}代碼中能根據(jù)租戶ID自動選擇數(shù)據(jù)源。
代碼一下子變得更優(yōu)雅了。
二、動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的原理
有些小伙伴在使用動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源時,可能只是簡單配置使用,并不清楚其底層工作原理。
理解核心原理對于排查問題和性能優(yōu)化至關(guān)重要。
下面跟大家一起聊聊動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的核心原理,希望對你會有所幫助。
數(shù)據(jù)源路由的核心機(jī)制
動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的核心在于AbstractRoutingDataSource,它是Spring框架提供的抽象類:
// Spring AbstractRoutingDataSource 源碼分析
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
// 目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)源映射表
private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
// 默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
// 解析后的數(shù)據(jù)源映射
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
// 解析后的默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源
private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
// 關(guān)鍵方法:確定當(dāng)前查找鍵
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
// 獲取連接時選擇數(shù)據(jù)源
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
}
// 確定目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)源
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
// 獲取查找鍵
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
// 根據(jù)查找鍵獲取數(shù)據(jù)源
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.resolvedDefaultDataSource != null || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
}
}線程安全的數(shù)據(jù)源上下文管理
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源上下文管理器 - 核心組件
* 使用ThreadLocal保證線程安全
*/
public class DataSourceContextHolder {
// 使用ThreadLocal保證線程隔離
private static final ThreadLocal<String> CONTEXT_HOLDER = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 支持嵌套數(shù)據(jù)源切換的棧
private static final ThreadLocal<Deque<String>> DATASOURCE_STACK = ThreadLocal.withInitial(ArrayDeque::new);
// 設(shè)置數(shù)據(jù)源
public static void setDataSource(String dataSource) {
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("數(shù)據(jù)源不能為null");
}
CONTEXT_HOLDER.set(dataSource);
// 同時壓入棧,支持嵌套調(diào)用
DATASOURCE_STACK.get().push(dataSource);
}
// 獲取當(dāng)前數(shù)據(jù)源
public static String getDataSource() {
return CONTEXT_HOLDER.get();
}
// 清除數(shù)據(jù)源
public static void clear() {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
Deque<String> stack = DATASOURCE_STACK.get();
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.pop();
// 如果棧中還有元素,恢復(fù)到上一個數(shù)據(jù)源
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.set(stack.peek());
}
}
}
// 強(qiáng)制清除所有上下文(用于線程池場景)
public static void clearCompletely() {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
DATASOURCE_STACK.get().clear();
}
// 判斷是否已設(shè)置數(shù)據(jù)源
public static boolean hasDataSource() {
return CONTEXT_HOLDER.get() != null;
}
}
/**
* 自定義路由數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
@Component
public class DynamicRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
// 所有可用的數(shù)據(jù)源
private final Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
String dataSourceKey = DataSourceContextHolder.getDataSource();
if (dataSourceKey == null) {
// 返回默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源
return "default";
}
// 驗(yàn)證數(shù)據(jù)源是否存在
if (!targetDataSources.containsKey(dataSourceKey)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("數(shù)據(jù)源 " + dataSourceKey + " 不存在");
}
logger.debug("當(dāng)前使用數(shù)據(jù)源: {}", dataSourceKey);
return dataSourceKey;
}
// 添加數(shù)據(jù)源
public void addDataSource(String key, DataSource dataSource) {
this.targetDataSources.put(key, dataSource);
// 更新目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)源映射
setTargetDataSources(new HashMap<>(this.targetDataSources));
// 重新初始化
afterPropertiesSet();
}
// 移除數(shù)據(jù)源
public void removeDataSource(String key) {
if (this.targetDataSources.containsKey(key)) {
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) this.targetDataSources.remove(key);
// 關(guān)閉數(shù)據(jù)源連接池
closeDataSource(dataSource);
// 更新目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)源映射
setTargetDataSources(new HashMap<>(this.targetDataSources));
afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
// 獲取所有數(shù)據(jù)源
public Map<Object, Object> getTargetDataSources() {
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(targetDataSources);
}
private void closeDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource instanceof HikariDataSource) {
((HikariDataSource) dataSource).close();
} else if (dataSource instanceof org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource) {
((org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource) dataSource).close();
}
// 其他類型的數(shù)據(jù)源關(guān)閉邏輯...
}
}動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源執(zhí)行流程
 圖片
圖片
三、基于Spring Boot的完整實(shí)現(xiàn)
有些小伙伴在配置動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源時可能會遇到各種問題,下面我提供一個生產(chǎn)級別的完整實(shí)現(xiàn)。
完整配置實(shí)現(xiàn)
/**
* 動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源配置類
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DynamicDataSourceProperties.class)
public class DynamicDataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
private DynamicDataSourceProperties properties;
/**
* 主數(shù)據(jù)源(默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源)
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 從數(shù)據(jù)源1
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave1")
public DataSource slave1DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 從數(shù)據(jù)源2
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave2")
public DataSource slave2DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSource dynamicDataSource(DataSource masterDataSource,
DataSource slave1DataSource,
DataSource slave2DataSource) {
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(8);
targetDataSources.put("master", masterDataSource);
targetDataSources.put("slave1", slave1DataSource);
targetDataSources.put("slave2", slave2DataSource);
DynamicRoutingDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicRoutingDataSource();
// 設(shè)置默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource);
// 設(shè)置目標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)源
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
/**
* 事務(wù)管理器
*/
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dynamicDataSource) {
returnnew DataSourceTransactionManager(dynamicDataSource);
}
/**
* MyBatis配置
*/
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dynamicDataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource);
// 配置MyBatis
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration configuration =
new org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration();
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true);
configuration.setCacheEnabled(true);
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(false);
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(false);
sessionFactory.setConfiguration(configuration);
return sessionFactory.getObject();
}
}
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源配置屬性類
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Data
public class DynamicDataSourceProperties {
/**
* 主數(shù)據(jù)源配置
*/
private HikariConfig master = new HikariConfig();
/**
* 從數(shù)據(jù)源1配置
*/
private HikariConfig slave1 = new HikariConfig();
/**
* 從數(shù)據(jù)源2配置
*/
private HikariConfig slave2 = new HikariConfig();
/**
* 動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源配置
*/
private DynamicConfig dynamic = new DynamicConfig();
@Data
public static class DynamicConfig {
/**
* 默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
private String primary = "master";
/**
* 是否開啟嚴(yán)格模式
*/
private boolean strict = false;
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源健康檢查間隔(秒)
*/
private long healthCheckInterval = 30;
}
}應(yīng)用配置文件
# application.yml
spring:
datasource:
# 動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源配置
dynamic:
primary:master
strict:true
health-check-interval:30
# 主數(shù)據(jù)源
master:
jdbc-url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/master_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username:root
password:master_password
driver-class-name:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
maximum-pool-size:20
minimum-idle:5
connection-timeout:30000
idle-timeout:600000
max-lifetime:1800000
pool-name:MasterHikariPool
# 從數(shù)據(jù)源1
slave1:
jdbc-url:jdbc:mysql://slave1:3306/slave_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username:root
password:slave1_password
driver-class-name:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
maximum-pool-size:15
minimum-idle:3
connection-timeout:30000
idle-timeout:600000
max-lifetime:1800000
pool-name:Slave1HikariPool
# 從數(shù)據(jù)源2
slave2:
jdbc-url:jdbc:mysql://slave2:3306/slave_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username:root
password:slave2_password
driver-class-name:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
maximum-pool-size:15
minimum-idle:3
connection-timeout:30000
idle-timeout:600000
max-lifetime:1800000
pool-name:Slave2HikariPool
# MyBatis配置
mybatis:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case:true
cache-enabled:true
lazy-loading-enabled:false
aggressive-lazy-loading:false注解式數(shù)據(jù)源切換
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源注解
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DataSource {
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源名稱
*/
String value() default "master";
/**
* 是否在方法執(zhí)行后清除數(shù)據(jù)源(默認(rèn)清除)
*/
boolean clear() default true;
}
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DataSourceAspect {
/**
* 定義切點(diǎn):所有標(biāo)注@DataSource注解的方法
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.annotation.DataSource)")
public void dataSourcePointCut() {}
/**
* 環(huán)繞通知:在方法執(zhí)行前后切換數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
@Around("dataSourcePointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
DataSource dataSourceAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
if (dataSourceAnnotation == null) {
// 類級別注解
dataSourceAnnotation = point.getTarget().getClass().getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
}
if (dataSourceAnnotation != null) {
String dataSourceKey = dataSourceAnnotation.value();
boolean clearAfter = dataSourceAnnotation.clear();
try {
log.debug("切換數(shù)據(jù)源到: {}", dataSourceKey);
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(dataSourceKey);
// 執(zhí)行原方法
return point.proceed();
} finally {
if (clearAfter) {
DataSourceContextHolder.clear();
log.debug("清除數(shù)據(jù)源上下文");
}
}
}
// 沒有注解,使用默認(rèn)數(shù)據(jù)源
return point.proceed();
}
}四、高級特性
有些小伙伴在基礎(chǔ)功能實(shí)現(xiàn)后,可能會遇到一些高級場景的需求。
下面介紹幾個生產(chǎn)環(huán)境中常用的高級特性。
讀寫分離自動路由
/**
* 讀寫分離數(shù)據(jù)源路由器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ReadWriteDataSourceRouter {
// 讀數(shù)據(jù)源列表
private final List<String> readDataSources = Arrays.asList("slave1", "slave2");
// 輪詢計(jì)數(shù)器
private final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 根據(jù)SQL自動選擇數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
public String determineDataSource(boolean isReadOperation) {
if (isReadOperation && !readDataSources.isEmpty()) {
// 讀操作:輪詢選擇從庫
int index = counter.getAndIncrement() % readDataSources.size();
if (counter.get() > 9999) {
counter.set(0); // 防止溢出
}
String readDataSource = readDataSources.get(index);
log.debug("讀操作選擇數(shù)據(jù)源: {}", readDataSource);
return readDataSource;
} else {
// 寫操作:選擇主庫
log.debug("寫操作選擇數(shù)據(jù)源: master");
return"master";
}
}
/**
* 根據(jù)SQL語句判斷是否為讀操作
*/
public boolean isReadOperation(String sql) {
if (sql == null) {
returntrue; // 默認(rèn)為讀操作
}
String trimmedSql = sql.trim().toLowerCase();
return trimmedSql.startsWith("select") ||
trimmedSql.startsWith("show") ||
trimmedSql.startsWith("explain");
}
}
/**
* MyBatis攔截器 - 自動讀寫分離
*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ReadWriteInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Autowired
private ReadWriteDataSourceRouter dataSourceRouter;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
String methodName = invocation.getMethod().getName();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
boolean isReadOperation = "query".equals(methodName);
String sql = getSql(ms, invocation.getArgs()[1]);
// 如果當(dāng)前沒有手動設(shè)置數(shù)據(jù)源,則自動選擇
if (!DataSourceContextHolder.hasDataSource()) {
String dataSource = dataSourceRouter.determineDataSource(isReadOperation);
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(dataSource);
try {
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
DataSourceContextHolder.clear();
}
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
private String getSql(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
return boundSql.getSql();
}
}多租戶數(shù)據(jù)源管理
/**
* 多租戶數(shù)據(jù)源管理器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class TenantDataSourceManager {
@Autowired
private DynamicRoutingDataSource dynamicRoutingDataSource;
@Autowired
private DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties;
// 租戶數(shù)據(jù)源配置緩存
private final Map<String, TenantDataSourceConfig> tenantConfigCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 根據(jù)租戶ID獲取數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
public DataSource getDataSourceForTenant(String tenantId) {
String dataSourceKey = "tenant_" + tenantId;
// 檢查是否已存在數(shù)據(jù)源
if (dynamicRoutingDataSource.getTargetDataSources().containsKey(dataSourceKey)) {
return (DataSource) dynamicRoutingDataSource.getTargetDataSources().get(dataSourceKey);
}
// 動態(tài)創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)源
synchronized (this) {
if (!dynamicRoutingDataSource.getTargetDataSources().containsKey(dataSourceKey)) {
DataSource dataSource = createTenantDataSource(tenantId);
dynamicRoutingDataSource.addDataSource(dataSourceKey, dataSource);
log.info("為租戶 {} 創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)源: {}", tenantId, dataSourceKey);
}
}
return (DataSource) dynamicRoutingDataSource.getTargetDataSources().get(dataSourceKey);
}
/**
* 動態(tài)創(chuàng)建租戶數(shù)據(jù)源
*/
private DataSource createTenantDataSource(String tenantId) {
TenantDataSourceConfig config = getTenantConfig(tenantId);
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(buildJdbcUrl(config));
dataSource.setUsername(config.getUsername());
dataSource.setPassword(config.getPassword());
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setMaximumPoolSize(10);
dataSource.setMinimumIdle(2);
dataSource.setConnectionTimeout(30000);
dataSource.setIdleTimeout(600000);
dataSource.setMaxLifetime(1800000);
dataSource.setPoolName("TenantPool_" + tenantId);
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 獲取租戶數(shù)據(jù)源配置(可從配置中心或數(shù)據(jù)庫獲取)
*/
private TenantDataSourceConfig getTenantConfig(String tenantId) {
return tenantConfigCache.computeIfAbsent(tenantId, key -> {
// 這里可以從配置中心、數(shù)據(jù)庫或緩存中獲取租戶配置
// 簡化實(shí)現(xiàn),實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中需要完善
TenantDataSourceConfig config = new TenantDataSourceConfig();
config.setHost("tenant-" + tenantId + ".db.example.com");
config.setPort(3306);
config.setDatabase("tenant_" + tenantId);
config.setUsername("tenant_" + tenantId);
config.setPassword("password_" + tenantId);
return config;
});
}
private String buildJdbcUrl(TenantDataSourceConfig config) {
return String.format("jdbc:mysql://%s:%d/%s?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&rewriteBatchedStatements=true",
config.getHost(), config.getPort(), config.getDatabase());
}
@Data
public static class TenantDataSourceConfig {
private String host;
private int port;
private String database;
private String username;
private String password;
}
}數(shù)據(jù)源健康監(jiān)控
/**
* 數(shù)據(jù)源健康監(jiān)控器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DataSourceHealthMonitor {
@Autowired
private DynamicRoutingDataSource dynamicRoutingDataSource;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
// 健康狀態(tài)緩存
private final Map<String, Boolean> healthStatus = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// 啟動健康檢查任務(wù)
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::checkAllDataSources, 0, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 檢查所有數(shù)據(jù)源的健康狀態(tài)
*/
public void checkAllDataSources() {
Map<Object, Object> dataSources = dynamicRoutingDataSource.getTargetDataSources();
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : dataSources.entrySet()) {
String dataSourceKey = (String) entry.getKey();
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) entry.getValue();
boolean isHealthy = checkDataSourceHealth(dataSource);
healthStatus.put(dataSourceKey, isHealthy);
if (!isHealthy) {
log.warn("數(shù)據(jù)源 {} 健康檢查失敗", dataSourceKey);
// 可以發(fā)送告警通知
}
}
}
/**
* 檢查單個數(shù)據(jù)源健康狀態(tài)
*/
private boolean checkDataSourceHealth(DataSource dataSource) {
try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement()) {
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT 1");
return rs.next() && rs.getInt(1) == 1;
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("數(shù)據(jù)源健康檢查異常", e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 獲取數(shù)據(jù)源健康狀態(tài)
*/
public boolean isDataSourceHealthy(String dataSourceKey) {
return healthStatus.getOrDefault(dataSourceKey, true);
}
/**
* 獲取健康的數(shù)據(jù)源列表
*/
public List<String> getHealthyDataSources() {
return healthStatus.entrySet().stream()
.filter(Map.Entry::getValue)
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
scheduler.shutdown();
}
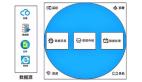
}五、動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的應(yīng)用場景
讓我們通過架構(gòu)圖來理解動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的典型應(yīng)用場景:
 圖片
圖片
六、優(yōu)缺點(diǎn)
優(yōu)點(diǎn)
- 靈活性高:支持運(yùn)行時動態(tài)添加、移除數(shù)據(jù)源
- 解耦性好:業(yè)務(wù)代碼與具體數(shù)據(jù)源解耦
- 擴(kuò)展性強(qiáng):易于實(shí)現(xiàn)讀寫分離、多租戶等復(fù)雜場景
- 維護(hù)方便:數(shù)據(jù)源配置集中管理,便于維護(hù)
缺點(diǎn)
- 復(fù)雜度增加:系統(tǒng)架構(gòu)變得更加復(fù)雜
- 事務(wù)管理復(fù)雜:跨數(shù)據(jù)源事務(wù)需要特殊處理
- 連接池開銷:每個數(shù)據(jù)源都需要獨(dú)立的連接池
- 調(diào)試?yán)щy:數(shù)據(jù)源切換增加了調(diào)試復(fù)雜度
七、生產(chǎn)環(huán)境注意事項(xiàng)
事務(wù)管理策略
/**
* 多數(shù)據(jù)源事務(wù)管理器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MultiDataSourceTransactionManager {
/**
* 在多個數(shù)據(jù)源上執(zhí)行事務(wù)性操作
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void executeInTransaction(Runnable task, String... dataSources) {
if (dataSources.length == 1) {
// 單數(shù)據(jù)源事務(wù)
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(dataSources[0]);
try {
task.run();
} finally {
DataSourceContextHolder.clear();
}
} else {
// 多數(shù)據(jù)源偽事務(wù)(最終一致性)
executeWithCompensation(task, dataSources);
}
}
/**
* 使用補(bǔ)償機(jī)制實(shí)現(xiàn)多數(shù)據(jù)源"事務(wù)"
*/
private void executeWithCompensation(Runnable task, String[] dataSources) {
List<Runnable> compensationTasks = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// 按順序執(zhí)行各個數(shù)據(jù)源的操作
for (String dataSource : dataSources) {
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(dataSource);
try {
// 執(zhí)行實(shí)際業(yè)務(wù)操作
task.run();
// 記錄補(bǔ)償操作
compensationTasks.add(0, createCompensationTask(dataSource));
} finally {
DataSourceContextHolder.clear();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 執(zhí)行補(bǔ)償操作
log.error("多數(shù)據(jù)源操作失敗,執(zhí)行補(bǔ)償操作", e);
executeCompensation(compensationTasks);
throw e;
}
}
private void executeCompensation(List<Runnable> compensationTasks) {
for (Runnable compensation : compensationTasks) {
try {
compensation.run();
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("補(bǔ)償操作執(zhí)行失敗", ex);
// 記錄補(bǔ)償失敗,需要人工介入
}
}
}
}性能優(yōu)化建議
- 連接池優(yōu)化:根據(jù)業(yè)務(wù)特點(diǎn)調(diào)整各數(shù)據(jù)源連接池參數(shù)
- 數(shù)據(jù)源預(yù)熱:應(yīng)用啟動時預(yù)熱常用數(shù)據(jù)源
- 緩存策略:緩存數(shù)據(jù)源配置和路由信息
- 監(jiān)控告警:建立完善的數(shù)據(jù)源監(jiān)控體系
總結(jié)
動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源是一個強(qiáng)大的技術(shù)方案,能夠很好地解決多數(shù)據(jù)源管理的復(fù)雜性。
通過本文的詳細(xì)解析,我們可以看到:
- 核心原理:基于
AbstractRoutingDataSource和ThreadLocal的上下文管理 - 實(shí)現(xiàn)方式:注解+AOP的聲明式數(shù)據(jù)源切換
- 高級特性:讀寫分離、多租戶、健康監(jiān)控等生產(chǎn)級功能
- 適用場景:多租戶、讀寫分離、分庫分表等復(fù)雜數(shù)據(jù)架構(gòu)
在實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中,建議根據(jù)具體業(yè)務(wù)需求選擇合適的實(shí)現(xiàn)方案,不要過度設(shè)計(jì)。
同時,要建立完善的監(jiān)控和運(yùn)維體系,確保動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)源的穩(wěn)定運(yùn)行。